进程启动概述
进程启动过程涉及到发起进程、system_server进程、zygote进程、被启动进程,它们的关系如下:
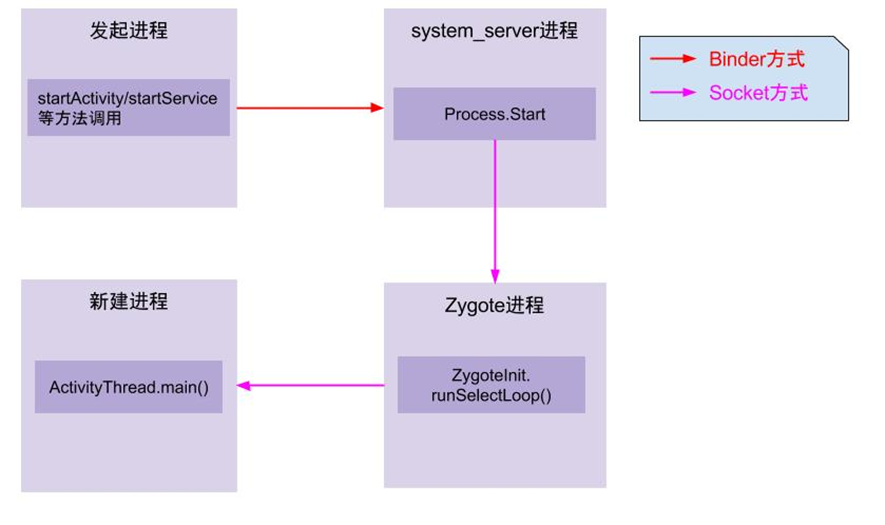
注:图片来自gityuan的博客
(1) App发起进程
当从桌面启动应用,则发起进程便是Launcher所在进程;当从某App内启动远程进程,则发送进程便是该App所在进程。发起进程先通过binder发送消息给system_server进程;
(2) system_server进程(AMS过程)
调用Process.start()方法,通过socket向zygote进程发送创建新进程的请求;
(3) zygote进程
在执行ZygoteInit.main()后便进入runSelectLoop()循环体内,当有客户端连接时便会执行ZygoteConnection.runOnce()方法,再经过层层调用后fork出新的应用进程;
(4) 新进程
执行handleChildProc方法,最后调用ActivityThread.main()方法。
接下来,依次从system_server进程发起请求到Zygote创建进程,再到新进程的运行这3大块展开讲解进程创建是一个怎样的过程。
AMS流程
Base on: Android T
Branch: android-13.0.0_r30
总流程
以桌面点击启动APP为例,堆栈如下。
AMS.startProcessLocked() ->
ProcessList.startProcessLocked(16 args) ->
ProcessList.startProcessLocked(4 args) ->
ProcessList.startProcessLocked(6 args) ->
ProcessList.startProcessLocked(14 args) ->
ProcessList.handleProcessStart() ->
ProcessList.startProcess() ->
AppZygote.getProcess().start()
AMS.startProcessLocked()
final ProcessRecord startProcessLocked(String processName,
ApplicationInfo info, boolean knownToBeDead, int intentFlags,
HostingRecord hostingRecord, int zygotePolicyFlags, boolean allowWhileBooting,
boolean isolated) {
return mProcessList.startProcessLocked(processName, info, knownToBeDead, intentFlags,
hostingRecord, zygotePolicyFlags, allowWhileBooting, isolated, 0 /* isolatedUid */,
false /* isSdkSandbox */, 0 /* sdkSandboxClientAppUid */,
null /* sdkSandboxClientAppPackage */,
null /* ABI override */, null /* entryPoint */,
null /* entryPointArgs */, null /* crashHandler */);
}
ProcessList.startProcessLocked(16 args)
ProcessList中有5个重载形式的startProcessLocked。
首先进入的参数多的那一个(有16个参数),通过newProcessRecordLocked获得一个ProcessRecord对象,然后把这个对象作为参数调用另一个重载的startProcessLocked()。
if (app == null) {
checkSlow(startTime, "startProcess: creating new process record");
app = newProcessRecordLocked(info, processName, isolated, isolatedUid, isSdkSandbox,
sdkSandboxUid, sdkSandboxClientAppPackage, hostingRecord);
if (app == null) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Failed making new process record for "
+ processName + "/" + info.uid + " isolated=" + isolated);
return null;
}
app.mErrorState.setCrashHandler(crashHandler);
app.setIsolatedEntryPoint(entryPoint);
app.setIsolatedEntryPointArgs(entryPointArgs);
if (predecessor != null) {
app.mPredecessor = predecessor;
predecessor.mSuccessor = app;
}
checkSlow(startTime, "startProcess: done creating new process record");
} else {
// If this is a new package in the process, add the package to the list
app.addPackage(info.packageName, info.longVersionCode, mService.mProcessStats);
checkSlow(startTime, "startProcess: added package to existing proc");
}
// If the system is not ready yet, then hold off on starting this
// process until it is.
if (!mService.mProcessesReady
&& !mService.isAllowedWhileBooting(info)
&& !allowWhileBooting) {
if (!mService.mProcessesOnHold.contains(app)) {
mService.mProcessesOnHold.add(app);
}
if (DEBUG_PROCESSES) Slog.v(TAG_PROCESSES,
"System not ready, putting on hold: " + app);
checkSlow(startTime, "startProcess: returning with proc on hold");
return app;
}
checkSlow(startTime, "startProcess: stepping in to startProcess");
final boolean success =
startProcessLocked(app, hostingRecord, zygotePolicyFlags, abiOverride);
checkSlow(startTime, "startProcess: done starting proc!");
return success ? app : null;
ProcessList.startProcessLocked(4 args)
@GuardedBy("mService")
boolean startProcessLocked(ProcessRecord app, HostingRecord hostingRecord,
int zygotePolicyFlags, String abiOverride) {
return startProcessLocked(app, hostingRecord, zygotePolicyFlags,
false /* disableHiddenApiChecks */, false /* disableTestApiChecks */,
abiOverride);
}
ProcessList.startProcessLocked(6 args)
该函数内代码较多,不多解释。在这里设置入口类并调用另一个startProcessLocked()。
// Start the process. It will either succeed and return a result containing
// the PID of the new process, or else throw a RuntimeException.
final String entryPoint = "android.app.ActivityThread";
return startProcessLocked(hostingRecord, entryPoint, app, uid, gids,
runtimeFlags, zygotePolicyFlags, mountExternal, seInfo, requiredAbi,
instructionSet, invokeWith, startUptime, startElapsedTime);
ProcessList.startProcessLocked(14 args)
@GuardedBy("mService")
boolean startProcessLocked(HostingRecord hostingRecord, String entryPoint, ProcessRecord app,
int uid, int[] gids, int runtimeFlags, int zygotePolicyFlags, int mountExternal,
String seInfo, String requiredAbi, String instructionSet, String invokeWith,
long startUptime, long startElapsedTime) {...}
// 关键代码
if (mService.mConstants.FLAG_PROCESS_START_ASYNC) {
if (DEBUG_PROCESSES) Slog.i(TAG_PROCESSES,
"Posting procStart msg for " + app.toShortString());
mService.mProcStartHandler.post(() -> handleProcessStart(
app, entryPoint, gids, runtimeFlags, zygotePolicyFlags, mountExternal,
requiredAbi, instructionSet, invokeWith, startSeq));
return true;
} else {
try {
final Process.ProcessStartResult startResult = startProcess(hostingRecord,
entryPoint, app,
uid, gids, runtimeFlags, zygotePolicyFlags, mountExternal, seInfo,
requiredAbi, instructionSet, invokeWith, startUptime);
handleProcessStartedLocked(app, startResult.pid, startResult.usingWrapper,
startSeq, false);
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
Slog.e(ActivityManagerService.TAG, "Failure starting process "
+ app.processName, e);
app.setPendingStart(false);
mService.forceStopPackageLocked(app.info.packageName, UserHandle.getAppId(app.uid),
false, false, true, false, false, app.userId, "start failure");
}
return app.getPid() > 0;
}
步骤:
- 如果是异步开启进程,则通过发送消息执行ProcessList.handleProcessStart();
- 如果是同步开启进程,则直接调用ProcessList.startProcess(),之后也会调用到appZygote.getProcess().start();
- 系统中比较常用异步开启进程,因为开启进程容易出现各种意外。
接下看异步开启进程的流程,实际上同步开启也差不多,只不过在不同线程。
ProcessList.handleProcessStart()
先创建一个Runnable对象,之后执行run()。
在这个startProcessLocked中,调用startProcess创建一个新的进程,将返回的Process.ProcessStartResult对象作为参数传入handleProcessStartedLocked()中。
/**
* Main handler routine to start the given process from the ProcStartHandler.
*
* <p>Note: this function doesn't hold the global AM lock intentionally.</p>
*/
private void handleProcessStart(final ProcessRecord app, final String entryPoint,
final int[] gids, final int runtimeFlags, int zygotePolicyFlags,
final int mountExternal, final String requiredAbi, final String instructionSet,
final String invokeWith, final long startSeq) {
final Runnable startRunnable = () -> {
try {
final Process.ProcessStartResult startResult = startProcess(app.getHostingRecord(),
entryPoint, app, app.getStartUid(), gids, runtimeFlags, zygotePolicyFlags,
mountExternal, app.getSeInfo(), requiredAbi, instructionSet, invokeWith,
app.getStartTime());
synchronized (mService) {
handleProcessStartedLocked(app, startResult, startSeq);
}
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
synchronized (mService) {
Slog.e(ActivityManagerService.TAG, "Failure starting process "
+ app.processName, e);
mPendingStarts.remove(startSeq);
app.setPendingStart(false);
mService.forceStopPackageLocked(app.info.packageName,
UserHandle.getAppId(app.uid),
false, false, true, false, false, app.userId, "start failure");
}
}
};
// Use local reference since we are not using locks here
final ProcessRecord predecessor = app.mPredecessor;
if (predecessor != null && predecessor.getDyingPid() > 0) {
handleProcessStartWithPredecessor(predecessor, startRunnable);
} else {
// Kick off the process start for real.
startRunnable.run();
}
}
ProcessList.startProcess()
startProcess()根据hostingRecord确定实际的进程启动方式:
- WebviewZygote: 辅助Zygote进程,用于创建 isolated_app 进程来渲染不可信的web内容,具有最为严格的安全限制;
- AppZygote: 应用Zygote进程,与常规Zygote创建的应用相比受到更多限制;
- regularZygote: 即常规的zygote32/zygote64 进程,是所有 Android Java应用的父进程,桌面点击开启进程就是走的regularZygote;
final Process.ProcessStartResult startResult;
boolean regularZygote = false;
if (hostingRecord.usesWebviewZygote()) {
startResult = startWebView(entryPoint,
app.processName, uid, uid, gids, runtimeFlags, mountExternal,
app.info.targetSdkVersion, seInfo, requiredAbi, instructionSet,
app.info.dataDir, null, app.info.packageName,
app.getDisabledCompatChanges(),
new String[]{PROC_START_SEQ_IDENT + app.getStartSeq()});
} else if (hostingRecord.usesAppZygote()) {
final AppZygote appZygote = createAppZygoteForProcessIfNeeded(app);
// We can't isolate app data and storage data as parent zygote already did that.
startResult = appZygote.getProcess().start(entryPoint,
app.processName, uid, uid, gids, runtimeFlags, mountExternal,
app.info.targetSdkVersion, seInfo, requiredAbi, instructionSet,
app.info.dataDir, null, app.info.packageName,
/*zygotePolicyFlags=*/ ZYGOTE_POLICY_FLAG_EMPTY, isTopApp,
app.getDisabledCompatChanges(), pkgDataInfoMap, allowlistedAppDataInfoMap,
false, false,
new String[]{PROC_START_SEQ_IDENT + app.getStartSeq()});
} else {
regularZygote = true;
startResult = Process.start(entryPoint,
app.processName, uid, uid, gids, runtimeFlags, mountExternal,
app.info.targetSdkVersion, seInfo, requiredAbi, instructionSet,
app.info.dataDir, invokeWith, app.info.packageName, zygotePolicyFlags,
isTopApp, app.getDisabledCompatChanges(), pkgDataInfoMap,
allowlistedAppDataInfoMap, bindMountAppsData, bindMountAppStorageDirs,
new String[]{PROC_START_SEQ_IDENT + app.getStartSeq()});
}
接下来以regularZygote为例。
Process.start()
全部代码如下,接下来会进入到Zygote中(但还未进入Zygote进程)。
public static ProcessStartResult start(@NonNull final String processClass,
@Nullable final String niceName,
int uid, int gid, @Nullable int[] gids,
int runtimeFlags,
int mountExternal,
int targetSdkVersion,
@Nullable String seInfo,
@NonNull String abi,
@Nullable String instructionSet,
@Nullable String appDataDir,
@Nullable String invokeWith,
@Nullable String packageName,
int zygotePolicyFlags,
boolean isTopApp,
@Nullable long[] disabledCompatChanges,
@Nullable Map<String, Pair<String, Long>>
pkgDataInfoMap,
@Nullable Map<String, Pair<String, Long>>
whitelistedDataInfoMap,
boolean bindMountAppsData,
boolean bindMountAppStorageDirs,
@Nullable String[] zygoteArgs) {
return ZYGOTE_PROCESS.start(processClass, niceName, uid, gid, gids,
runtimeFlags, mountExternal, targetSdkVersion, seInfo,
abi, instructionSet, appDataDir, invokeWith, packageName,
zygotePolicyFlags, isTopApp, disabledCompatChanges,
pkgDataInfoMap, whitelistedDataInfoMap, bindMountAppsData,
bindMountAppStorageDirs, zygoteArgs);
}
Zygote流程
Base on: Android T
Branch: android-13.0.0_r30
参数处理
在发送数据到Zygote进程前,还需要处理创建进程的一系列参数。
ZygoteProcess.start() ->
ZygoteProcess.startViaZygote() ->
ZygoteProcess.zygoteSendArgsAndGetResult() ->
ZygoteProcess.attemptZygoteSendArgsAndGetResult() ->
private Process.ProcessStartResult attemptZygoteSendArgsAndGetResult(
ZygoteState zygoteState, String msgStr) throws ZygoteStartFailedEx {
try {
final BufferedWriter zygoteWriter = zygoteState.mZygoteOutputWriter;
final DataInputStream zygoteInputStream = zygoteState.mZygoteInputStream;
zygoteWriter.write(msgStr);
zygoteWriter.flush();
// Always read the entire result from the input stream to avoid leaving
// bytes in the stream for future process starts to accidentally stumble
// upon.
Process.ProcessStartResult result = new Process.ProcessStartResult();
result.pid = zygoteInputStream.readInt();
result.usingWrapper = zygoteInputStream.readBoolean();
if (result.pid < 0) {
throw new ZygoteStartFailedEx("fork() failed");
}
return result;
} catch (IOException ex) {
zygoteState.close();
Log.e(LOG_TAG, "IO Exception while communicating with Zygote - "
+ ex.toString());
throw new ZygoteStartFailedEx(ex);
}
}
attemptZygoteSendArgsAndGetResult()方法的主要功能是通过socket通道向Zygote进程发送一个参数列表,即zygoteWriter.write(msgStr),然后进入阻塞等待状态,直到远端的socket服务端发送回来新创建的进程pid才返回。
接下来就是Zygote进程的流程。
Zygote进程
ZygoteConnection.processCommand() ->
ZygoteConnection.handleChildProc() ->
ZygoteInit.zygoteInit() ->
RuntimeInit.applicationInit() ->
RuntimeInit.findStaticMain() ->
new MethodAndArgsCaller(m, argv)
通过反射调用ActivityThread.main()方法。
ZygoteConnection.processCommand()
Zygote通过processCommand()循环接收命令,接收到后进行参数处理。
/**
* Reads a command from the command socket. If a child is successfully forked, a
* {@code Runnable} that calls the childs main method (or equivalent) is returned in the child
* process. {@code null} is always returned in the parent process (the zygote).
* If multipleOK is set, we may keep processing additional fork commands before returning.
*
* If the client closes the socket, an {@code EOF} condition is set, which callers can test
* for by calling {@code ZygoteConnection.isClosedByPeer}.
*/
Runnable processCommand(ZygoteServer zygoteServer, boolean multipleOK) {...}
创建进程的关键流程:
- 通过Zygote.forkAndSpecialize()创建进程,具体情况略;
- 如果是创建子进程,则执行handleChildProc(parsedArgs, descriptors, childPipeFd, newStderr)。
执行进程创建的关键代码:
if (parsedArgs.mInvokeWith != null || parsedArgs.mStartChildZygote
|| !multipleOK || peer.getUid() != Process.SYSTEM_UID) {
// Continue using old code for now. TODO: Handle these cases in the other path.
pid = Zygote.forkAndSpecialize(parsedArgs.mUid, parsedArgs.mGid,
parsedArgs.mGids, parsedArgs.mRuntimeFlags, rlimits,
parsedArgs.mMountExternal, parsedArgs.mSeInfo, parsedArgs.mNiceName,
fdsToClose, fdsToIgnore, parsedArgs.mStartChildZygote,
parsedArgs.mInstructionSet, parsedArgs.mAppDataDir,
parsedArgs.mIsTopApp, parsedArgs.mPkgDataInfoList,
parsedArgs.mAllowlistedDataInfoList, parsedArgs.mBindMountAppDataDirs,
parsedArgs.mBindMountAppStorageDirs);
try {
if (pid == 0) {
// in child
zygoteServer.setForkChild();
zygoteServer.closeServerSocket();
IoUtils.closeQuietly(serverPipeFd);
serverPipeFd = null;
return handleChildProc(parsedArgs, childPipeFd,
parsedArgs.mStartChildZygote);
} else {
// In the parent. A pid < 0 indicates a failure and will be handled in
// handleParentProc.
IoUtils.closeQuietly(childPipeFd);
childPipeFd = null;
handleParentProc(pid, serverPipeFd);
return null;
}
} finally {
IoUtils.closeQuietly(childPipeFd);
IoUtils.closeQuietly(serverPipeFd);
}
}
ZygoteConnection.handleChildProc()
/**
* Handles post-fork setup of child proc, closing sockets as appropriate,
* reopen stdio as appropriate, and ultimately throwing MethodAndArgsCaller
* if successful or returning if failed.
*
* @param parsedArgs non-null; zygote args
* @param pipeFd null-ok; pipe for communication back to Zygote.
* @param isZygote whether this new child process is itself a new Zygote.
*/
private Runnable handleChildProc(ZygoteArguments parsedArgs,
FileDescriptor pipeFd, boolean isZygote) {
/*
* By the time we get here, the native code has closed the two actual Zygote
* socket connections, and substituted /dev/null in their place. The LocalSocket
* objects still need to be closed properly.
*/
closeSocket();
Zygote.setAppProcessName(parsedArgs, TAG);
// End of the postFork event.
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
if (parsedArgs.mInvokeWith != null) {
WrapperInit.execApplication(parsedArgs.mInvokeWith,
parsedArgs.mNiceName, parsedArgs.mTargetSdkVersion,
VMRuntime.getCurrentInstructionSet(),
pipeFd, parsedArgs.mRemainingArgs);
// Should not get here.
throw new IllegalStateException("WrapperInit.execApplication unexpectedly returned");
} else {
if (!isZygote) {
return ZygoteInit.zygoteInit(parsedArgs.mTargetSdkVersion,
parsedArgs.mDisabledCompatChanges,
parsedArgs.mRemainingArgs, null /* classLoader */);
} else {
return ZygoteInit.childZygoteInit(
parsedArgs.mRemainingArgs /* classLoader */);
}
}
}
这里的isZygote=false,在ZygoteProcess.start()中设定的。所以接下来走ZygoteInit.zygoteInit()流程。
ZygoteInit.zygoteInit()
/**
* The main function called when started through the zygote process. This could be unified with
* main(), if the native code in nativeFinishInit() were rationalized with Zygote startup.<p>
*
* Current recognized args:
* <ul>
* <li> <code> [--] <start class name> <args>
* </ul>
*
* @param targetSdkVersion target SDK version
* @param disabledCompatChanges set of disabled compat changes for the process (all others
* are enabled)
* @param argv arg strings
*/
public static Runnable zygoteInit(int targetSdkVersion, long[] disabledCompatChanges,
String[] argv, ClassLoader classLoader) {
if (RuntimeInit.DEBUG) {
Slog.d(RuntimeInit.TAG, "RuntimeInit: Starting application from zygote");
}
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "ZygoteInit");
RuntimeInit.redirectLogStreams();
RuntimeInit.commonInit();
ZygoteInit.nativeZygoteInit();
return RuntimeInit.applicationInit(targetSdkVersion, disabledCompatChanges, argv,
classLoader);
}
RuntimeInit.applicationInit()
protected static Runnable applicationInit(int targetSdkVersion, long[] disabledCompatChanges,
String[] argv, ClassLoader classLoader) {
// If the application calls System.exit(), terminate the process
// immediately without running any shutdown hooks. It is not possible to
// shutdown an Android application gracefully. Among other things, the
// Android runtime shutdown hooks close the Binder driver, which can cause
// leftover running threads to crash before the process actually exits.
nativeSetExitWithoutCleanup(true);
VMRuntime.getRuntime().setTargetSdkVersion(targetSdkVersion);
VMRuntime.getRuntime().setDisabledCompatChanges(disabledCompatChanges);
final Arguments args = new Arguments(argv);
// The end of of the RuntimeInit event (see #zygoteInit).
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
// Remaining arguments are passed to the start class's static main
return findStaticMain(args.startClass, args.startArgs, classLoader);
}
RuntimeInit.findStaticMain()
通过反射调用被启动进程的ActivityThread.main()方法。
在MethodAndArgsCaller(m, argv)中:
- m = cl.getMethod(“main”, new Class[] { String[].class });
- argv即android.app.ActivityThread类,是在ProcessList.startProcessLocked(6 args)中确定的。
/**
* Invokes a static "main(argv[]) method on class "className".
* Converts various failing exceptions into RuntimeExceptions, with
* the assumption that they will then cause the VM instance to exit.
*
* @param className Fully-qualified class name
* @param argv Argument vector for main()
* @param classLoader the classLoader to load {@className} with
*/
protected static Runnable findStaticMain(String className, String[] argv,
ClassLoader classLoader) {
Class<?> cl;
try {
cl = Class.forName(className, true, classLoader);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Missing class when invoking static main " + className,
ex);
}
Method m;
try {
m = cl.getMethod("main", new Class[] { String[].class });
} catch (NoSuchMethodException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Missing static main on " + className, ex);
} catch (SecurityException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Problem getting static main on " + className, ex);
}
int modifiers = m.getModifiers();
if (! (Modifier.isStatic(modifiers) && Modifier.isPublic(modifiers))) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Main method is not public and static on " + className);
}
/*
* This throw gets caught in ZygoteInit.main(), which responds
* by invoking the exception's run() method. This arrangement
* clears up all the stack frames that were required in setting
* up the process.
*/
return new MethodAndArgsCaller(m, argv);
}
APP端流程
Base on: Android T
Branch: android-13.0.0_r30
总流程
ActivityThread.main() ->
ActivityThread.attach() ->
AMS.attachApplication() ->
AMS.attachApplicationLocked() ->
AT.ApplicationThread.bindApplication() ->
AT.handleBindApplication() ->
LoadedApk.makeApplication() ->
Instrumentation.newApplication()
关键过程如下。
ActivityThread.main()
在ActivityThread.main中,主要完成以下工作:
- 创建主线程的Looper对象;
- 创建ActivityThread对象thread = new ActivityThread();
- thread.attach(false, startSeq)是当前主线程向system_server进程通信的过程, 将thread信息告知AMS;
- sMainThreadHandler = thread.getHandler(),获取主线程的handler对象。
public static void main(String[] args) {
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "ActivityThreadMain");
// Install selective syscall interception
AndroidOs.install();
// CloseGuard defaults to true and can be quite spammy. We
// disable it here, but selectively enable it later (via
// StrictMode) on debug builds, but using DropBox, not logs.
CloseGuard.setEnabled(false);
Environment.initForCurrentUser();
// Make sure TrustedCertificateStore looks in the right place for CA certificates
final File configDir = Environment.getUserConfigDirectory(UserHandle.myUserId());
TrustedCertificateStore.setDefaultUserDirectory(configDir);
// Call per-process mainline module initialization.
initializeMainlineModules();
Process.setArgV0("<pre-initialized>");
Looper.prepareMainLooper();
// Find the value for {@link #PROC_START_SEQ_IDENT} if provided on the command line.
// It will be in the format "seq=114"
long startSeq = 0;
if (args != null) {
for (int i = args.length - 1; i >= 0; --i) {
if (args[i] != null && args[i].startsWith(PROC_START_SEQ_IDENT)) {
startSeq = Long.parseLong(
args[i].substring(PROC_START_SEQ_IDENT.length()));
}
}
}
ActivityThread thread = new ActivityThread();
thread.attach(false, startSeq);
if (sMainThreadHandler == null) {
sMainThreadHandler = thread.getHandler();
}
if (false) {
Looper.myLooper().setMessageLogging(new
LogPrinter(Log.DEBUG, "ActivityThread"));
}
// End of event ActivityThreadMain.
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
Looper.loop();
throw new RuntimeException("Main thread loop unexpectedly exited");
}
ActivityThread.attach()
private void attach(boolean system, long startSeq) {
sCurrentActivityThread = this;
mConfigurationController = new ConfigurationController(this);
mSystemThread = system;
if (!system) {
android.ddm.DdmHandleAppName.setAppName("<pre-initialized>",
UserHandle.myUserId());
RuntimeInit.setApplicationObject(mAppThread.asBinder());
final IActivityManager mgr = ActivityManager.getService();
try {
mgr.attachApplication(mAppThread, startSeq);
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
throw ex.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
// Watch for getting close to heap limit.
BinderInternal.addGcWatcher(new Runnable() {
@Override public void run() {
if (!mSomeActivitiesChanged) {
return;
}
Runtime runtime = Runtime.getRuntime();
long dalvikMax = runtime.maxMemory();
long dalvikUsed = runtime.totalMemory() - runtime.freeMemory();
if (dalvikUsed > ((3*dalvikMax)/4)) {
if (DEBUG_MEMORY_TRIM) Slog.d(TAG, "Dalvik max=" + (dalvikMax/1024)
+ " total=" + (runtime.totalMemory()/1024)
+ " used=" + (dalvikUsed/1024));
mSomeActivitiesChanged = false;
try {
ActivityTaskManager.getService().releaseSomeActivities(mAppThread);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
throw e.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
}
}
});
} else {...}
//...
}
AMS.attachApplicationLocked()
private boolean attachApplicationLocked(@NonNull IApplicationThread thread,
int pid, int callingUid, long startSeq) {...}
attachApplicationLocked()代码比较复杂,在Android T中大概有500行。但其主要功能有两个:创建Application和启动其它三大组件。
(1) 创建Application
thread.bindApplication(processName, appInfo,
app.sdkSandboxClientAppVolumeUuid, app.sdkSandboxClientAppPackage,
providerList, null, profilerInfo, null, null, null, testMode,
mBinderTransactionTrackingEnabled, enableTrackAllocation,
isRestrictedBackupMode || !normalMode, app.isPersistent(),
new Configuration(app.getWindowProcessController().getConfiguration()),
app.getCompat(), getCommonServicesLocked(app.isolated),
mCoreSettingsObserver.getCoreSettingsLocked(),
buildSerial, autofillOptions, contentCaptureOptions,
app.getDisabledCompatChanges(), serializedSystemFontMap,
app.getStartElapsedTime(), app.getStartUptime());
(2) 拉起组件
如果进程是因为Activity、Broadcast、Service拉起的,在创建进程后,在attachApplicationLocked()中拉起这些组件。
注意:Provider是随APP启动的,其启动过程在AT.handleBindApplication()中,比Application.onCreate()和其它组件要早。
// See if the top visible activity is waiting to run in this process...
if (normalMode) {
try {
didSomething = mAtmInternal.attachApplication(app.getWindowProcessController());
} catch (Exception e) {
Slog.wtf(TAG, "Exception thrown launching activities in " + app, e);
badApp = true;
}
}
// Find any services that should be running in this process...
if (!badApp) {
try {
didSomething |= mServices.attachApplicationLocked(app, processName);
checkTime(startTime, "attachApplicationLocked: after mServices.attachApplicationLocked");
} catch (Exception e) {
Slog.wtf(TAG, "Exception thrown starting services in " + app, e);
badApp = true;
}
}
if (!badApp) {
updateUidReadyForBootCompletedBroadcastLocked(app.uid);
}
// Check if a next-broadcast receiver is in this process...
if (!badApp && isPendingBroadcastProcessLocked(pid)) {
try {
didSomething |= sendPendingBroadcastsLocked(app);
checkTime(startTime, "attachApplicationLocked: after sendPendingBroadcastsLocked");
} catch (Exception e) {
// If the app died trying to launch the receiver we declare it 'bad'
Slog.wtf(TAG, "Exception thrown dispatching broadcasts in " + app, e);
badApp = true;
}
}
AT.ApplicationThread.bindApplication()
在这里将相关参数封装到AppBindData对象中,然后通过H.BIND_APPLICATION消息发送到ActivityThread。
public final void bindApplication(String processName, ApplicationInfo appInfo,
String sdkSandboxClientAppVolumeUuid, String sdkSandboxClientAppPackage,
ProviderInfoList providerList, ComponentName instrumentationName,
ProfilerInfo profilerInfo, Bundle instrumentationArgs,
IInstrumentationWatcher instrumentationWatcher,
IUiAutomationConnection instrumentationUiConnection, int debugMode,
boolean enableBinderTracking, boolean trackAllocation,
boolean isRestrictedBackupMode, boolean persistent, Configuration config,
CompatibilityInfo compatInfo, Map services, Bundle coreSettings,
String buildSerial, AutofillOptions autofillOptions,
ContentCaptureOptions contentCaptureOptions, long[] disabledCompatChanges,
SharedMemory serializedSystemFontMap,
long startRequestedElapsedTime, long startRequestedUptime) {
if (services != null) {
if (false) {
// Test code to make sure the app could see the passed-in services.
for (Object oname : services.keySet()) {
if (services.get(oname) == null) {
continue; // AM just passed in a null service.
}
String name = (String) oname;
// See b/79378449 about the following exemption.
switch (name) {
case "package":
case Context.WINDOW_SERVICE:
continue;
}
if (ServiceManager.getService(name) == null) {
Log.wtf(TAG, "Service " + name + " should be accessible by this app");
}
}
}
// Setup the service cache in the ServiceManager
ServiceManager.initServiceCache(services);
}
setCoreSettings(coreSettings);
AppBindData data = new AppBindData();
data.processName = processName;
data.appInfo = appInfo;
data.sdkSandboxClientAppVolumeUuid = sdkSandboxClientAppVolumeUuid;
data.sdkSandboxClientAppPackage = sdkSandboxClientAppPackage;
data.providers = providerList.getList();
data.instrumentationName = instrumentationName;
data.instrumentationArgs = instrumentationArgs;
data.instrumentationWatcher = instrumentationWatcher;
data.instrumentationUiAutomationConnection = instrumentationUiConnection;
data.debugMode = debugMode;
data.enableBinderTracking = enableBinderTracking;
data.trackAllocation = trackAllocation;
data.restrictedBackupMode = isRestrictedBackupMode;
data.persistent = persistent;
data.config = config;
data.compatInfo = compatInfo;
data.initProfilerInfo = profilerInfo;
data.buildSerial = buildSerial;
data.autofillOptions = autofillOptions;
data.contentCaptureOptions = contentCaptureOptions;
data.disabledCompatChanges = disabledCompatChanges;
data.mSerializedSystemFontMap = serializedSystemFontMap;
data.startRequestedElapsedTime = startRequestedElapsedTime;
data.startRequestedUptime = startRequestedUptime;
sendMessage(H.BIND_APPLICATION, data);
}
AT.handleBindApplication()
由ActivityThread.H.handleMessage()执行H.BIND_APPLICATION消息调用而来。
case BIND_APPLICATION:
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "bindApplication");
AppBindData data = (AppBindData)msg.obj;
handleBindApplication(data);
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
break;
handleBindApplication()的代码也比较多,Android T中大约400行。handleBindApplication()主要进行了以下工作。
(1) 设置进程名,初始化一些策略和参数信息
(2) 创建Application对象
// If the app is being launched for full backup or restore, bring it up in
// a restricted environment with the base application class.
app = data.info.makeApplicationInner(data.restrictedBackupMode, null);
// Propagate autofill compat state
app.setAutofillOptions(data.autofillOptions);
// Propagate Content Capture options
app.setContentCaptureOptions(data.contentCaptureOptions);
sendMessage(H.SET_CONTENT_CAPTURE_OPTIONS_CALLBACK, data.appInfo.packageName);
mInitialApplication = app;
(3) 安装ContentProvider
同时,如果该Application声明了ContentProvider,还需要为该进程安装ContentProvider。ContentProvider..onCreate()执行在Application.onCreate()之前。
// don't bring up providers in restricted mode; they may depend on the
// app's custom Application class
if (!data.restrictedBackupMode) {
if (!ArrayUtils.isEmpty(data.providers)) {
installContentProviders(app, data.providers);
}
}
(4) 调用Application.onCreate()
try {
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "app.onCreate");
mInstrumentation.callApplicationOnCreate(app);
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!mInstrumentation.onException(app, e)) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to create application " + app.getClass().getName()
+ ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
}
LoadedApk.makeApplication()
public Application makeApplicationInner(boolean forceDefaultAppClass,
Instrumentation instrumentation) {
return makeApplicationInner(forceDefaultAppClass, instrumentation,
/* allowDuplicateInstances= */ false);
}
private Application makeApplicationInner(boolean forceDefaultAppClass,
Instrumentation instrumentation, boolean allowDuplicateInstances) {...}
Instrumentation.newApplication()
public Application newApplication(ClassLoader cl, String className, Context context)
throws InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException,
ClassNotFoundException {
Application app = getFactory(context.getPackageName())
.instantiateApplication(cl, className);
app.attach(context);
return app;
}