概述
组件与进程的关系
每个组件(如Activity、Service等四大组件)都运行在某一个进程中,一个进程中可以有多个组件。
常用术语:
- Server:服务端,表示运行服务的进程;
- Service:服务,运行于Server中的具体服务类,包含一系列方法;
- Client:客户端,使用系统服务的进程;
- Client组件:运行于Client中的具体组件,如Activity等。
AIDL生成Java文件
source build/envsetup.sh # 导入make命令
make aidl # 编译并安装aidl模块
# 将aidl文件转换为java文件,需要指明aidl命令所在路径
out/host/linux-x86/bin/aidl ./path/IMyService.aidl
最后在IMyService.aidl的同级目录下生成了IMyService.java文件。
其它命令及参数:
out/host/linux-x86/bin/aidl # 查看aidl命令说明
Binder相关术语
(1) Binder实体
Binder实体就是指各个Server以及ServiceManager在内核中的存在形式。也可以理解为在进程中实际存在的对象,包括我们真正的需要调用的方法。毕竟找到内核中的实体也就可以调用该实体在用户进程中对应的对象了。
在Binder模型中,每一个Server在Binder驱动中都对应一个Binder实体对象(binder_node结构体),用以描述它在内核中的状态。
(2) Binder引用
顾名思义,引用就是是位于本进程或其它进程中的指向实体的指针。而Binder引用实际上是内核中binder_ref结构体的对象。
Binder实体和Binder引用都是内核(即,Binder驱动)中的数据结构。每一个Server在内核中就表现为一个Binder实体,而每一个Client则表现为一个Binder引用。这样,每个Binder引用都对应一个Binder实体,而每个Binder实体则可以多个Binder引用。
(3) Binder本地对象
指Server提供的服务本身,或者指本进程中的对象。
(4) Binder代理对象
就是服务的代理。
(5) 强指针与弱指针
Native层中Binder实现
在实际通信过程中,各个进程都需要通过Binder传递消息。Android系统在Framework层中将各种对Binder驱动的操作封装成一个Binder库。
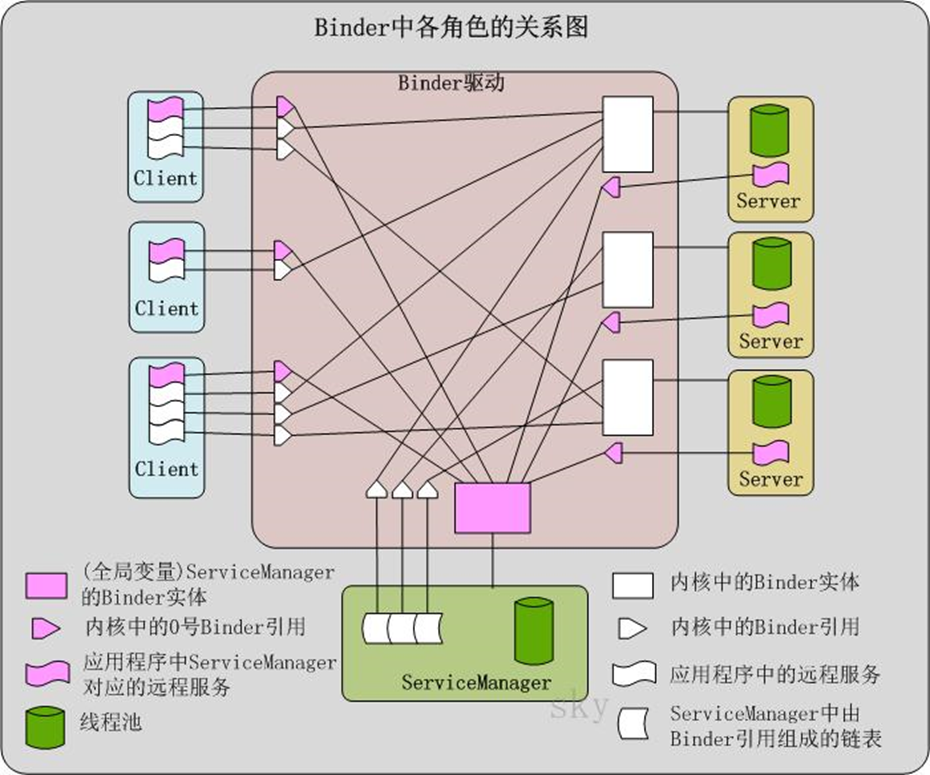
注:上图来自其它博客。
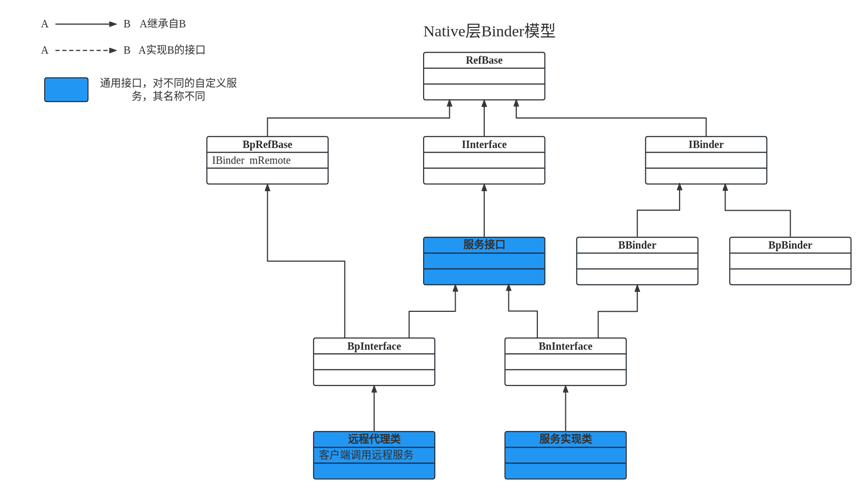
上图是Native层中Binder模型图,包含Server和Client部分的相关类图,大多数类的头文件位于frameworks/native/include/binder/(或者在frameworks/native/libs/binder/include/binder/),实现文件位于 /frameworks/native/libs/binder/。
图中,”本地服务”是Server提供的服务本身,而“远程服务”就是服务的代理,”服务接口”则是它们需要实现的通用接口。
在native层中,Binder是C/S架构,分为Bn端(Server)和Bp端(Client)。
RefBase
文件路径:/frameworks/rs/cpp/util/RefBase.h
说明:其子类的对象均可以通过强指针和弱指针来维护它们的生命周期。通过智能指针,Binder本地对象就可以通过引用计数技术来维护生命周期。
BpRefBase
文件路径:/frameworks/native/libs/binder/include/binder/Binder.h。
说明:为Binder代理对象提供了抽象的进程间通信接口,
主要方法为:
class BpRefBase : public virtual RefBase
{
protected:
explicit BpRefBase(const sp<IBinder>& o);
virtual ~BpRefBase();
virtual void onFirstRef();
virtual void onLastStrongRef(const void* id);
virtual bool onIncStrongAttempted(uint32_t flags, const void* id);
inline IBinder* remote() { return mRemote; }
inline IBinder* remote() const { return mRemote; }
private:
BpRefBase(const BpRefBase& o);
BpRefBase& operator=(const BpRefBase& o);
IBinder* const mRemote;
RefBase::weakref_type* mRefs;
std::atomic<int32_t> mState;
};
BpRefBase类有一个重要的成员变量mRemote,它指向一个BpBinder对象(实现了进程间通信接口),可以通过成员函数remote()来获取。
IInterface
源码路径:/frameworks/native/libs/binder/include/binder/IInterface.h
说明:由进程自定义的Service组件接口
class IInterface : public virtual RefBase
{
public:
IInterface();
static sp<IBinder> asBinder(const IInterface*);
static sp<IBinder> asBinder(const sp<IInterface>&);
protected:
virtual ~IInterface();
virtual IBinder* onAsBinder() = 0;
};
IBinder
源码路径:frameworks/native/libs/binder/include/binder/IBinder.h
说明:定义了为在提供进程间和跨进程间的调用时提供高性能的轻量级远程调用的核心部分。该接口描述了与远程对象进行交互的抽象协议。
BBinder
源码路径:/frameworks/native/libs/binder/include/binder/Binder.h
说明:BBinder为Binder本地对象提供了抽象的进程间通信接口。
class BBinder : public IBinder
{
public:
BBinder();
//…
// NOLINTNEXTLINE(google-default-arguments)
virtual status_t transact( uint32_t code,
const Parcel& data,
Parcel* reply,
uint32_t flags = 0) final;
//…
protected:
virtual ~BBinder();
// NOLINTNEXTLINE(google-default-arguments)
virtual status_t onTransact( uint32_t code,
const Parcel& data,
Parcel* reply,
uint32_t flags = 0);
};
当一个Binder代理对象通过Binder驱动向一个Binder本地对象发出一个进程间通信请求时,Binder驱动程序就会调用该Binder本地对象的成员函数transact()来处理该请求。
成员函数onTransact()负责分发与业务相关的进程间通信请求,由BBinder的子类(即Binder本地对象类)来实现的。
BpBinder
源码路径:/frameworks/native/libs/binder/include/binder/BpBinder.h
说明:BpBinder类实现了BpRefBase类的进程间通信接口。
class BpBinder : public IBinder
{
public:
int32_t handle() const;
// NOLINTNEXTLINE(google-default-arguments)
virtual status_t transact( uint32_t code,
const Parcel& data,
Parcel* reply,
uint32_t flags = 0) final;
//…
protected:
BpBinder(int32_t handle,int32_t trackedUid);
private:
const int32_t mHandle;
//…
};
BpBinder类的成员变量mHandle是一个int32_t类型的整数,它表示一个Client组件的句柄值,可以通过成员函数handle()来获取。
BpBinder类的成员函数transact()用来向运行在Server进程中的Service组件发送进程间通信请求,这是通过Binder驱动程序间接实现的。
transact()会把BpBinder类的成员变量mHandle以及进程间通信数据发送给Binder弥动程序,这样Binder驱动程序就能够根据这个句柄值来找到对应的Binder引用对象,继而找到对应的Binder实体对象,最后就可以将进程间通信数据发送给对应的Service组件了。
注:每一个Client中的组件在Binder驱动程序中都拥有一个Binder引用对象(binder_ref结构体),而每一个Binder引用对象都有一个句柄值,Client组件就是通过这个句柄值来和Binder驱动程序中的Binder引用对象建立对应关系的。
BnInterface
源码路径:/frameworks/native/libs/binder/include/binder/IInterface.h
template<typename INTERFACE>
class BnInterface : public INTERFACE, public BBinder
{
public:
virtual sp<IInterface> queryLocalInterface(const String16& _descriptor);
virtual const String16& getInterfaceDescriptor() const;
protected:
typedef INTERFACE BaseInterface;
virtual IBinder* onAsBinder();
};
BnInterface是一个模板类,模板参数INTERFACE是一个由进程自定义的Service组件接口,模板类Bnlnterface和Bpinterface都需要实现该接口。Binder本地对象类继承Bnlnterface。
BpInterface
BpInterface也是一个模板类,Binder代理对象类需要继承BpInterface。
IPCThreadState
源码路径:/frameworks/native/libs/binder/include/binder/IPCThreadState.h
class IPCThreadState {
public:
static IPCThreadState* self();
status_t transact(int32_t handle,
uint32_t code, const Parcel&data,
Parcel*reply, uint32_t flags);
private:
IPCThreadState();
~IPCThreadState();
status_t sendReply(const Parcel&reply, uint32_t flags);
status_t waitForResponse(Parcel *reply,
status_t *acquireResult=nullptr);
status_t talkWithDriver(bool doReceive=true);
const sp<ProcessState> mProcess;
}
每一个使用了Binder通信机制的进程都有一个Binder线程池(binder_proc->threads)用来处理进程间通信请求。对于每一个Binder线程来说,它的内部都有一个IPCThreadState对象,可以通过IPCThreadState类的静态成员函数self()来获取,并且调用IPCThreadState类的成员函数transanct()来和Binder驱动程序交互。
在IPCThreadState类的成员函数transanct()内部,与Binder驱动程序的交互操作又是通过调用成员函数talkWithDriver()来实现的,它一方面负责向Binder驱动程序发送进程间通信请求,另一方面又负责接收来自Binder驱动程序的进程间通信请求。
ProcessState
源码路径:/frameworks/native/libs/binder/include/binder/ProcessState.h
IPCThreadState类有一个成员变量mProcess,它指向一个ProcessState对象。 对于每一个使用了Binder进程间通信机制的进程来说,它的内部都有一个ProcessState对象.
ProcessState负责初始化Binder设备,即打开设备文件/dev/binder,以及将设备文件/dev/binder映射到进程的地址空间。 ProcessState对象在进程范围内是唯一的,所以Binder线程池中的每一个线程都可以通过它来和Binder驱动程序建立连接。
class ProcessState : public virtual RefBase
{
public:
static sp<ProcessState> self();
static sp<ProcessState> selfOrNull();
static sp<ProcessState> initWithDriver(const char *driver);
private:
friend class IPCThreadState;
explicit ProcessState(const char* driver);
~ProcessState();
.......
String8 mDriverName;
int mDriverFD;
void* mVMStart;
};
进程中的ProcessState对象可以通过ProcessState类的静态成员函数self()来获取。 第一次调用ProcessState类的静态成员函数self()时,Binder库就会为进程创建一个ProcessState对象,并且调用函数open()来打开设备文件“/dev/binder”,接着又调用函数mmap()将映射到进程的地址空间,即请求Binder驱动程序为进程分配内核缓冲区。设备文件/dev/binder映射到进程的地址空间后,得到的内核缓冲区的用户地址就保存在其成员变量mVMStart中。
Framework层中Binder实现
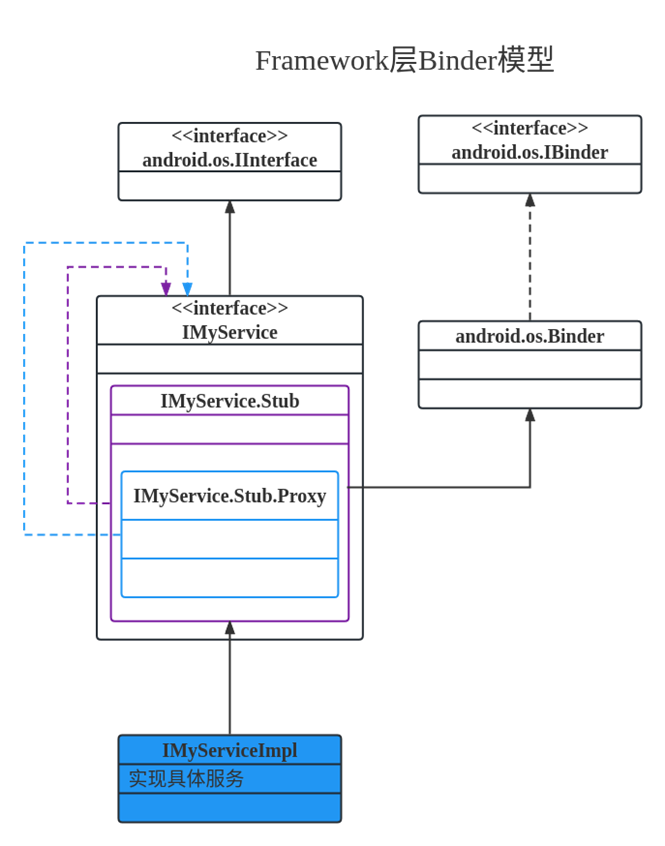
| 类 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| IMyService | 相当于Native层中继承IInterface的用户自定义的服务接口 |
| IMyService.Stub | 相当于Native层中的BnInterface,服务的实现类需要继承它 |
| IMyService.Stub.Proxy | 相当于Native层中的BpInterface。客户端通过获取到代理对象实现对服务端的调用 |
IInterface
源码路径:frameworks/base/core/java/android/os/IInterface.java
package android.os;
/**
* Base class for Binder interfaces. When defining a new interface,
* you must derive it from IInterface.
*/
public interface IInterface
{
/**
* Retrieve the Binder object associated with this interface.
* You must use this instead of a plain cast, so that proxy objects
* can return the correct result.
*/
public IBinder asBinder();
}
IBinder
源码路径:frameworks/base/core/java/android/os/IBinder.java
作用:相当于Native层中的BBinder。
public interface IBinder {
/**
* The first transaction code available for user commands.
*/
int FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION = 0x00000001;
/**
* The last transaction code available for user commands.
*/
int LAST_CALL_TRANSACTION = 0x00ffffff;
//...
/**
* Get the canonical name of the interface supported by this binder.
*/
public @Nullable
String getInterfaceDescriptor() throws RemoteException;
public @Nullable
IInterface queryLocalInterface(@NonNull String descriptor);
//...
public boolean transact(int code, @NonNull Parcel data, @Nullable Parcel reply, int flags)
throws RemoteException;
public interface DeathRecipient {
public void binderDied();
default void binderDied(IBinder who) {
binderDied();
}
}
}
AIDL生成的Java文件说明
IMyService.java代码
/*
* This file is auto-generated. DO NOT MODIFY.
*/
public interface IMyService extends android.os.IInterface
{
/** Default implementation for IMyService. */
public static class Default implements IMyService
{
@Override public void sayHello() throws android.os.RemoteException
{
}
@Override
public android.os.IBinder asBinder() {
return null;
}
}
/** Local-side IPC implementation stub class. */
public static abstract class Stub extends android.os.Binder implements IMyService
{
private static final java.lang.String DESCRIPTOR = "IMyService";
/** Construct the stub at attach it to the interface. */
public Stub()
{
this.attachInterface(this, DESCRIPTOR);
}
/**
* Cast an IBinder object into an IMyService interface,
* generating a proxy if needed.
*/
public static IMyService asInterface(android.os.IBinder obj)
{
if ((obj==null)) {
return null;
}
android.os.IInterface iin = obj.queryLocalInterface(DESCRIPTOR);
if (((iin!=null)&&(iin instanceof IMyService))) {
return ((IMyService)iin);
}
return new IMyService.Stub.Proxy(obj);
}
@Override public android.os.IBinder asBinder()
{
return this;
}
@Override public boolean onTransact(int code, android.os.Parcel data, android.os.Parcel reply, int flags) throws android.os.RemoteException
{
java.lang.String descriptor = DESCRIPTOR;
switch (code)
{
case INTERFACE_TRANSACTION:
{
reply.writeString(descriptor);
return true;
}
case TRANSACTION_sayHello:
{
data.enforceInterface(descriptor);
this.sayHello();
reply.writeNoException();
return true;
}
default:
{
return super.onTransact(code, data, reply, flags);
}
}
}
private static class Proxy implements IMyService
{
private android.os.IBinder mRemote;
Proxy(android.os.IBinder remote)
{
mRemote = remote;
}
@Override public android.os.IBinder asBinder()
{
return mRemote;
}
public java.lang.String getInterfaceDescriptor()
{
return DESCRIPTOR;
}
@Override public void sayHello() throws android.os.RemoteException
{
android.os.Parcel _data = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
android.os.Parcel _reply = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
try {
_data.writeInterfaceToken(DESCRIPTOR);
boolean _status = mRemote.transact(Stub.TRANSACTION_sayHello, _data, _reply, 0);
if (!_status && getDefaultImpl() != null) {
getDefaultImpl().sayHello();
return;
}
_reply.readException();
}
finally {
_reply.recycle();
_data.recycle();
}
}
public static IMyService sDefaultImpl;
}
static final int TRANSACTION_sayHello = (android.os.IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION + 0);
public static boolean setDefaultImpl(IMyService impl) {
// Only one user of this interface can use this function
// at a time. This is a heuristic to detect if two different
// users in the same process use this function.
if (Stub.Proxy.sDefaultImpl != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("setDefaultImpl() called twice");
}
if (impl != null) {
Stub.Proxy.sDefaultImpl = impl;
return true;
}
return false;
}
public static IMyService getDefaultImpl() {
return Stub.Proxy.sDefaultImpl;
}
}
public void sayHello() throws android.os.RemoteException;
}
IMyService.java文件里有3个类:
(1)IMyService接口
定义:public interface IMyService extends android.os.IInterface
(2) 空实现类Default
定义:public static class Default implements IMyService
(3)抽象类IMyService.stub
定义:public static abstract class Stub extends android.os.Binder implements IMyService
(4)代理类IMyService.Stub.Proxy
定义:private static class Proxy implements IMyService
IMyService的继承关系
IMyService继承于/frameworks/base/core/java/android/os/IInterface.java类,IInterface.java代码如下:
package android.os;
/**
* Base class for Binder interfaces. When defining a new interface,
* you must derive it from IInterface.
*/
public interface IInterface
{
/**
* Retrieve the Binder object associated with this interface.
* You must use this instead of a plain cast, so that proxy objects
* can return the correct result.
*/
public IBinder asBinder();
}
IBinder也是一个接口类,其定义及关键方法如下:
package android.os;
import android.annotation.NonNull;
import android.annotation.Nullable;
import android.compat.annotation.UnsupportedAppUsage;
import java.io.FileDescriptor;
public interface IBinder {
//..........(属性)
//..........(接口方法)
/**
* Get the canonical name of the interface supported by this binder.
*/
public @Nullable String getInterfaceDescriptor() throws RemoteException;
//........
/**
* Perform a generic operation with the object.
*
* @param code The action to perform. This should
* be a number between {@link #FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION} and
* {@link #LAST_CALL_TRANSACTION}.
* @param data Marshalled data to send to the target. Must not be null.
* If you are not sending any data, you must create an empty Parcel
* that is given here.
* @param reply Marshalled data to be received from the target. May be
* null if you are not interested in the return value.
* @param flags Additional operation flags. Either 0 for a normal
* RPC, or {@link #FLAG_ONEWAY} for a one-way RPC.
*
* @return Returns the result from {@link Binder#onTransact}. A successful call
* generally returns true; false generally means the transaction code was not
* understood.
*/
public boolean transact(int code, @NonNull Parcel data, @Nullable Parcel reply, int flags)
throws RemoteException;
}
IMyService类
除了内部类之外,仅声明了需要代理类和服务类实现的接口函数:
public void sayHello() throws android.os.RemoteException;
Default—空实现类
定义:public static class Default implements IMyService
作用:未知
IMyService.Stub
定义:public static abstract class Stub extends android.os.Binder implements IMyService
作用:IMyService.stub是一个静态抽象类。服务实现类继承此类,然后实现服务中的具体方法。表示服务端接口。
IMyService.Stub继承于android.os.Binder类和IMyService接口。Binder类则实现了android.os.IBinder接口。IMyService.Stub未实现IMyService接口中声明的方法,需要具体的实现类来定义。
注:在内部类中使用this表示内部类实例。
IMyService.Stub中的成员如下:
- 静态常量:private static final java.lang.String DESCRIPTOR;
- 静态常量:static final int TRANSACTION_sayHello;
- 构造函数内的方法:this.attachInterface(this, DESCRIPTOR);
- 成员函数:static IMyService asInterface(android.os.IBinder obj)
- 成员函数:public android.os.IBinder asBinder()
- 成员函数:public boolean onTransact(int code, android.os.Parcel data, android.os.Parcel reply, int flags)
- 静态函数:public static boolean setDefaultImpl(IMyService impl);
- 静态函数:public static IMyService getDefaultImpl();
(1) DESCRIPTOR
静态成员变量DESCRIPTOR,用来描述接口的名称。
(2) attachInterface(this, DESCRIPTOR)
IMyService.Stub构造函数如下:
public Stub()
{
this.attachInterface(this, DESCRIPTOR);
}
//attachInterface()的定义在Binder类中:
private IInterface mOwner;
private String mDescriptor;
public void attachInterface(IInterface owner, String descriptor) {
mOwner = owner;
mDescriptor = descriptor;
}
该方法用于将当前的Interface与Binder联系起来,由于传递了DESCRIPTOR这个参数,唯一标识了当前Interface。
(3) asInterface(IBinder obj)
功能:静态成员函数aslnterface通常用来将一个Java服务代理对象(即IBinder对象)封装成一个IFregService.Stub.Proxy对象,Proxy是一个实现了IFregService接口的Java服务代理对象。
代码如下:
public static IMyService asInterface(android.os.IBinder obj)
{
if ((obj==null)) {
return null;
}
android.os.IInterface iin = obj.queryLocalInterface(DESCRIPTOR);
if (((iin!=null)&&(iin instanceof IMyService))) {
return ((IMyService)iin);
}
return new IMyService.Stub.Proxy(obj);
}
asInterface()的参数为一个IBinder接口对象,该对象来自客户端调用服务的代码:
// 通过服务名获取服务的引用
IBinder binder = ServiceManager.getService("server.myservice");
//通过引用获取代理对象
IMyService myService = IMyService.Stub.asInterface(binder);
//通过代理对象调用接口的方法
myService.sayHello();
在asInterface()调用客户端的IBinder对象的queryLocalInterface(DESCRIPTOR)方法:
private IInterface mOwner;
private String mDescriptor;
public IInterface queryLocalInterface(String descriptor) {
if (mDescriptor != null && mDescriptor.equals(descriptor)) {
return mOwner;
}
return null;
}
该方法会在本进程中查找descriptor,如果客户端通过注册服务名获取的IBinder引用对象的descriptor与所请求的服务的IBinder引用对象的DESCRIPTOR相同的话,则返回obj的IInterface对象iin。
iin instanceof IMyService用于判断iin是否是IMyService的一个实例(或子类),显然不是。所以执行return new IMyService.Stub.Proxy(obj),返回代理对象。
(4) asBinder()
代码如下:
@Override public android.os.IBinder asBinder()
{
return this;
}
返回IBinder类型的自身的引用。
(4) onTransact(int code, Parcel data, Parcel reply, int flags)
功能:成员函数onTransact是用来接收和分发进程间通信请求的,并调用代理类中的服务函数。
IMyService.Stub.Proxy
定义:private static class Proxy implements IMyService
类IMyService.Stub.Proxy是在Java抽象类IMyService.Stub内部定义的。IMyService.Stub.Proxy类用来描述一个Java服务代理对象,Proxy类实现了IMyService接口的实现代理的成员函数。
IMyService.Stub.Proxy中的成员如下:
- 属性:private android.os.IBinder mRemote;
- 构造函数内的方法:mRemote = remote;
- 成员函数:public android.os.IBinder asBinder()
- 成员函数:public java.lang.String getInterfaceDescriptor()
- 成员函数:public void sayHello()
- 静态属性:public static IMyService sDefaultImpl;